Federal Reserve Interest Rate History
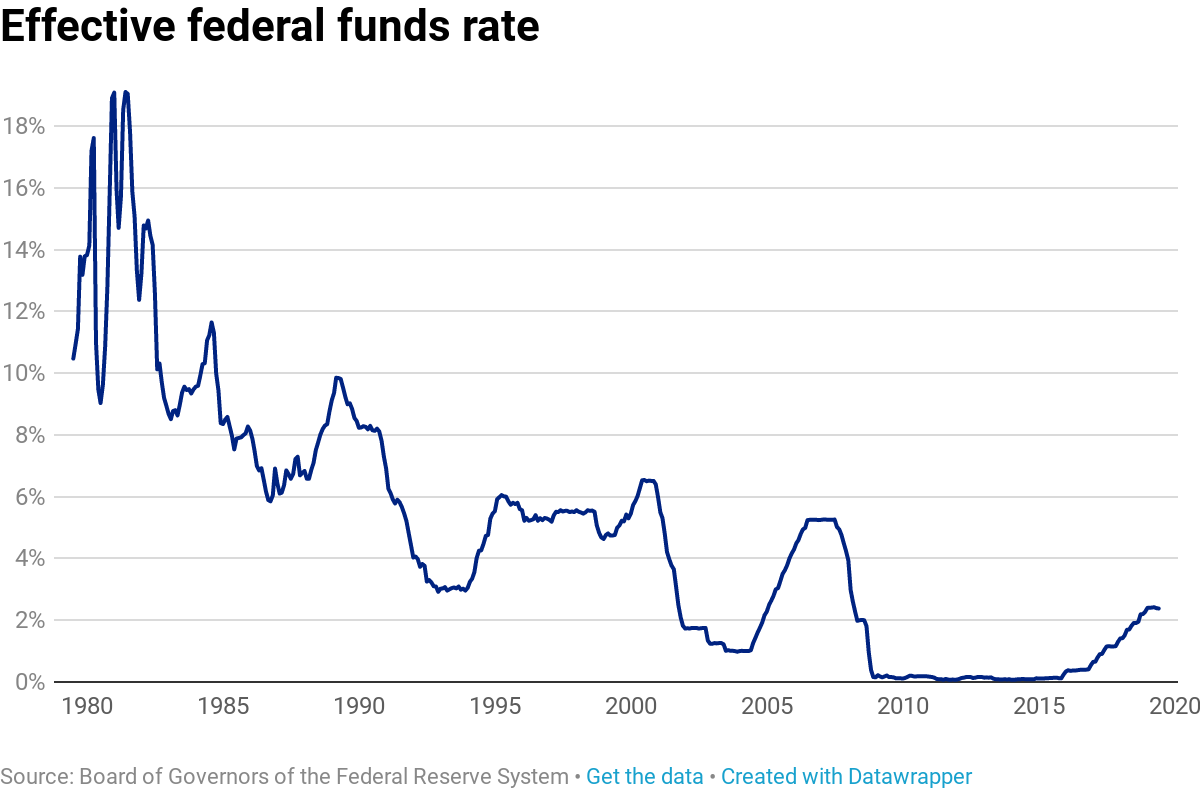
Federal reserve interest rates – The Federal Reserve (Fed) is the central bank of the United States and has the primary responsibility for conducting the nation’s monetary policy. One of the key tools used by the Fed to influence the economy is the federal funds rate, which is the interest rate at which banks lend money to each other overnight.
The Federal Reserve’s interest rate decisions have far-reaching implications, affecting everything from consumer spending to economic growth. For instance, a recent study explored the impact of interest rate changes on the outcome of the argentina vs ecuador football match, highlighting the complex interplay between financial markets and sporting events.
Understanding these connections can help us better navigate the uncertainties of the global economy and make informed decisions about our financial future.
The Fed has a long history of adjusting interest rates to achieve its economic goals, which include price stability, maximum employment, and moderate long-term interest rates. Over the years, the Fed has made numerous changes to the federal funds rate in response to changing economic conditions.
The Federal Reserve’s decision to raise interest rates has sparked concerns about its impact on the economy. While the central bank aims to curb inflation, some fear it could lead to a recession. Amidst these economic uncertainties, a TikToker was fired after posting a video criticizing her company’s handling of the interest rate hike.
The incident highlights the potential consequences of expressing dissent in an era of economic turmoil.
Timeline of Key Interest Rate Changes
Here is a timeline of some of the most significant interest rate changes made by the Fed:
- 1979: The Fed raised interest rates to a record high of 20% in an effort to combat high inflation.
- 1980: The Fed lowered interest rates to 10% as the economy entered a recession.
- 1987: The Fed raised interest rates to 9% in an effort to prevent the economy from overheating.
- 1990: The Fed lowered interest rates to 6% as the economy entered a recession.
- 1994: The Fed raised interest rates to 6% in an effort to combat rising inflation.
- 2000: The Fed lowered interest rates to 6% as the economy entered a recession.
- 2007: The Fed raised interest rates to 5.25% in an effort to prevent the economy from overheating.
- 2008: The Fed lowered interest rates to 0% as the economy entered a recession.
- 2015: The Fed raised interest rates to 0.25% as the economy began to recover.
- 2018: The Fed raised interest rates to 2.25% in an effort to combat rising inflation.
- 2020: The Fed lowered interest rates to 0% as the economy entered a recession due to the COVID-19 pandemic.
Factors Influencing Interest Rate Changes
The Fed considers a number of factors when making decisions about interest rates, including:
- Economic growth: The Fed wants to keep the economy growing at a moderate pace.
- Inflation: The Fed wants to keep inflation low and stable.
- Unemployment: The Fed wants to keep unemployment low.
- Financial stability: The Fed wants to ensure that the financial system is stable and resilient.
Impact of Interest Rate Changes on the Economy, Federal reserve interest rates
Changes in interest rates can have a significant impact on the economy.
Federal Reserve interest rates have a significant impact on global economies. While the US economy is likely to see a moderate increase in rates, the Colombian economy is expected to remain relatively stable. For a more detailed analysis of the differences between the two countries, visit usa vs colombia.
Returning to the topic of interest rates, it is important to note that the Federal Reserve’s decision will have far-reaching implications for both domestic and international markets.
- Higher interest rates: Higher interest rates can slow economic growth by making it more expensive for businesses to borrow money and invest.
- Lower interest rates: Lower interest rates can stimulate economic growth by making it less expensive for businesses to borrow money and invest.
| Date | Interest Rate | Reason for Change | Impact on Economy |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1979 | 20% | To combat high inflation | Slowed economic growth |
| 1980 | 10% | As the economy entered a recession | Stimulated economic growth |
| 1987 | 9% | To prevent the economy from overheating | Slowed economic growth |
| 1990 | 6% | As the economy entered a recession | Stimulated economic growth |
| 1994 | 6% | To combat rising inflation | Slowed economic growth |
| 2000 | 6% | As the economy entered a recession | Stimulated economic growth |
| 2007 | 5.25% | To prevent the economy from overheating | Slowed economic growth |
| 2008 | 0% | As the economy entered a recession | Stimulated economic growth |
| 2015 | 0.25% | As the economy began to recover | Stimulated economic growth |
| 2018 | 2.25% | To combat rising inflation | Slowed economic growth |
| 2020 | 0% | As the economy entered a recession due to the COVID-19 pandemic | Stimulated economic growth |
Impact of Interest Rates on the Economy

Interest rates are a crucial tool used by central banks to influence economic activity. They have a significant impact on various aspects of the economy, including inflation, consumer spending, business investment, and economic growth.
Interest Rates and Inflation
Interest rates play a vital role in managing inflation. When inflation is high, central banks typically raise interest rates to curb economic growth and reduce demand. This makes borrowing more expensive, discouraging businesses from expanding and consumers from making large purchases. As a result, demand for goods and services decreases, which helps bring inflation under control.
Interest Rates and Consumer Spending
Interest rates have a direct impact on consumer spending. When interest rates are low, borrowing becomes more affordable, encouraging consumers to make purchases. This can lead to increased demand for goods and services, stimulating economic growth. Conversely, when interest rates are high, borrowing becomes more expensive, reducing consumer spending and slowing down economic activity.
Interest Rates and Business Investment
Interest rates also affect business investment. Low interest rates make it cheaper for businesses to borrow funds for expansion, research and development, and new equipment. This can lead to increased productivity and economic growth. However, when interest rates are high, businesses may be less willing to invest, which can hinder economic progress.
Historical Examples
Historically, changes in interest rates have had a significant impact on the economy. For example, the Federal Reserve’s aggressive interest rate hikes in the early 1980s helped bring down inflation but also led to a severe recession. In contrast, the low interest rates during the 1990s and 2000s contributed to economic growth and prosperity.
Future Outlook for Interest Rates: Federal Reserve Interest Rates

The future path of interest rates is uncertain, but the Federal Reserve has indicated that it plans to continue raising rates in the coming months. This is in response to the high inflation rate, which is currently at a 40-year high. The Fed’s goal is to bring inflation down to its target of 2%.
The impact of future interest rate changes on businesses, consumers, and the overall economy will depend on the magnitude and timing of the changes. If the Fed raises rates too quickly, it could lead to a recession. However, if the Fed raises rates too slowly, inflation could continue to rise, which would also damage the economy.
Factors Influencing Federal Reserve’s Decision-Making on Interest Rates
- The rate of inflation
- The unemployment rate
- The level of economic growth
- The global economic outlook
- The actions of other central banks
Federal Reserve interest rates have been on a steady upward trajectory, causing concern among economists. Francisco Alvarez , a renowned economist, has expressed concerns about the impact of rising interest rates on economic growth. However, the Federal Reserve remains committed to its strategy of raising rates to combat inflation.
The Federal Reserve’s recent interest rate hike has sent shockwaves through global markets. While the impact on developed economies is still being debated, it is clear that emerging markets like méxico brasil will be particularly vulnerable. With their high levels of foreign debt and dependence on foreign investment, these countries are likely to see their currencies depreciate and their economies slow down.
The full extent of the damage remains to be seen, but it is clear that the Federal Reserve’s actions will have a significant impact on the global economy.